

When the Sun, Moon and Earth come into a straight line an ECLIPSE
occurs. This does not happen very often because the Moon's orbit is inclined to that of the
Earth. A TOTAL eclipse occurs when all the Moon or Sun is blotted out. A PARTIAL eclipse
is when only part of the Sun or Moon is covered.

The Moon passes into
the shadow of the Earth, it ever completely disappears because a small amount of the Sun's
light is refracted by the Earth's atmosphere and falls on the Moon during the
eclipse. This light gives the Moon a reddish appearance.
You can see form Figure 1
that at the distance of the Moon the Earth's shadow is much bigger than the Moon and so
the Moon takes some time to pass through it.
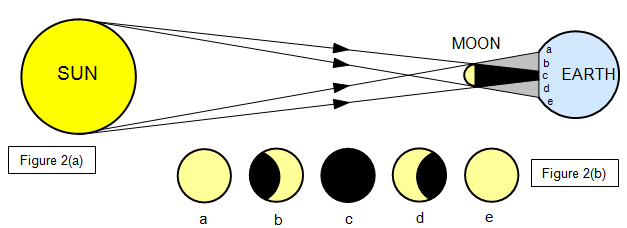
Figure 2(b) shows the view of the Sun from the Earth during the eclipse. Diagram (c) shows the total eclipse. The shadow of the Moon falls on the Earth and because the Moon and Earth are moving compared with the Sun this shadow moves across the Earth's surface during an eclipse.