
The diagram shows a typical house hot water system. You can follow the temperature of the water around the system - red for hot water and blue for cold water. Notice that there are two separate circuits. One for water used for washing and drinking and another for water used in the central heating.
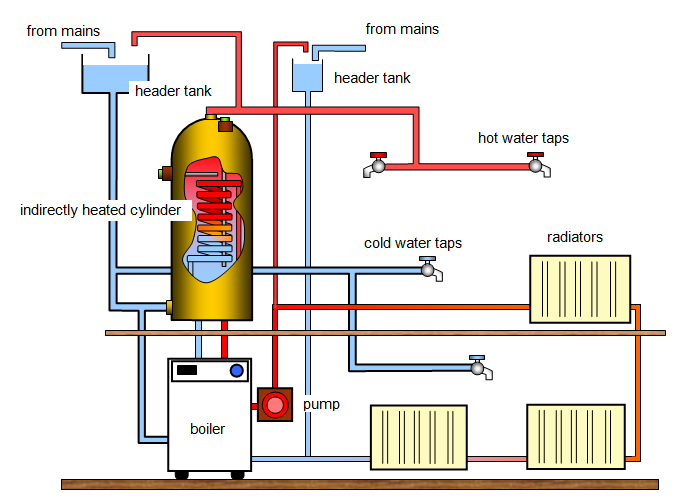
As you know the hot water rises to the top due to convection and this would meant that all the downstairs radiators and hot taps would get cold. To stop this happening an electric pump is used to keep the water moving round the system to make sure that downstairs does not get cold. So, if there is a power cut your central heating would not work because although the boiler might light (probably not because the programmer would stop) the electric pump would not work.
Notice the indirectly heated hot water cylinder. Hot water from the boiler flows through a coil in the cylinder and heat from this is transferred to the rest of the cylinder. There will also usually be an electric immersion heater which you can use to heat the water when the boiler is off.
There are also header or expansion tanks. These collect excess water due to expansion in the pipes.