Lenses
A lens is a specially shaped piece of glass, plastic or other
transparent material that is used to give an image. Even a drop of water can act as a
lens.
Lens types
The five main types of lens are drawn below:
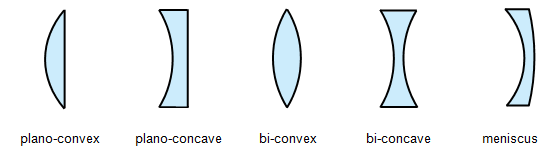
We usually refer to lenses as either
convex or concave. A lens that is convex on both sides should really be called bi-convex and one that is concave on both sides is bi-concave.
The meniscus lens behaves as either a convex or a concave lens depending on which side
is the more sharply curved.
You can easily see the difference in the behaviour of convex and concave lenses. If you hold a convex lens in front of some writing then the writing will
look bigger, but through a concave lens it will look smaller.
Images with
lenses
Both types of lens produce images but they may be of different types. You
can show this easily by trying to focus an image onto a piece of paper. With a convex lens
you will get an upside down real image but with the concave lens the image is
virtual.
Convex lens
Convex lenses converge or concentrate light to a
focus if the image is further from the lens that its focal length.
What is it like to look
through?
1 Close to object - it magnifies.
2 Far from eye - image upside
down.
Uses of convex lenses Eye, camera,
overhead projector, focus sunlight, projector
microscope, simple telescope,
glasses (to correct for long sight), magnifying glass

schoolphysics: Convex lens animation
To see an animation of the action of a convex lens click on the animation link.
Concave
lens
Concave lenses diverge or spread out the light. There is no real focus. Image
is always virtual. Power is negative.
What is it like to look through?
The image
that you see is always the right way up and smaller.
Uses of concave
lenses Glasses (to correct for short sight), spy holes in doors,
some telescopes,
back window of coaches
A VERSION IN WORD IS AVAILABLE ON THE SCHOOLPHYSICS USB