Paying for Electricity
Leaving on a 1.5 kW electric fire all night will use TEN TIMES as much energy as a 150 W light bulb left on for the same time.
"You can't watch TV all evening it will cost too much”
A new car battery costs a lot of money, partly because of the electrical energy stored inside it!
Some people may get very cold in the winter because they cannot afford to heat their homes using electric fires
The Christmas lights in many towns are very expensive to run
A guesthouse charges a visitor 50 p for a hot bath
Electricity, or rather electrical
energy costs money. We pay for it when we buy a battery and we pay the electricity board for the
electricity that we use from the mains.
The average electricity bill for a house in a year would
probably be about £500, although this very much depends on how the house is
heated.
The electricity board measures the electrical energy that we use not in joules but
in units called KILOWATT-HOURS.
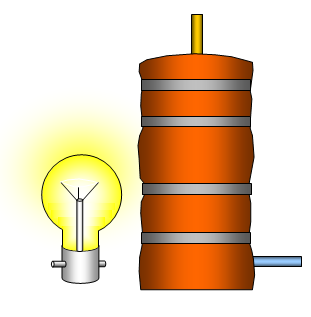
A kilowatt-hour (kWh) is the energy that a one kilowatt appliance uses in one hour
One kilowatt
hour = 1000 W x 3600 s
= 1000 x 3600
= 3 600 000
J
At the moment (2010) this amount of electricity costs about 15p in Britain although this depends on how much energy you use and the cost is changing all the time.
The power is
measured in kilowatts and the time in hours. So a 1 kW electric fire will use 5 kWh in 5 hours
but a 100 W light bulb will only use 5 kWh if it is on for 50 hours.
Cost = Electrical power x time x cost per kWh
Example problems
Cost per kWh = 15p.
1. Calculate the cost of running a 2 kW grill for 20 minutes
Cost = 2 x 0.33 x 15 = 10 p
2. Calculate the cost of running a 150 W light bulb for 3 hours
Cost = 0.15 x 3 x 15 = 6.75 p
A kilowatt-hour (kWh) is also called a UNIT of electrical
energy by the electricity boards.
Student investigation
Try and work out and compare the cost of running a torch from a battery and from the mains. Which will cost more per kWh?
PROBLEMS
Take the cost of 1 kWh to be 15p.
1. What does the electrical energy cost
to run:
(a) a 3 kW immersion heater for 20 m
(b) a 200 W light bulb for 24 hours
(c) a 2 kW fire
for 4 hours a day for 3 months
2. How long can you use the following for 10p
(a) a 2 kW fire
(b)
a 4 kW cooker ring
(c) a 150 W light bulb
(d) a 250 W TV
3. Copy and complete the following
table:
| 10 |
Appliance |
Power |
Time |
Cost |
10 |
Appliance |
Power |
Time |
Cost |
| 1 |
Kettle |
2.5 kW |
6 min |
|
6 |
Light bulb |
60 W |
4 hours |
|
| 2 |
Iron |
|
2 hours |
30 p |
7 |
Light bulb |
|
3 hours |
9 p |
| 3 |
Washing machine |
250 W |
45 min |
|
8 |
Hair drier |
0.15 kW |
|
5 p |
| 4 |
Stereo |
200 W |
|
15 p |
9 |
Vacuum cleaner |
0.5 kW |
|
15 p |
| 5 |
Television |
|
4 hours |
22.5 p |
10 |
Freezer |
120 W |
6 hours |
|
Power and time
Since appliances are
usually marked with the power at which they run we can work out how much energy they will use
in a certain time. We can do this using the formula:
Power = Energy/Time
which when rearranged becomes:
Energy = Power x Time
[Power in watts, time in seconds,
energy in joules]
A normal house will use about 15 000 MJ of energy in a year.
Example problems
1. How much energy is used by a 150 W black and white television if is left on for 4 hours?
Energy = Power x time = 150 x 4 x 60 x 60
= 2160 000 = 2.16 MJ
2. How much energy is used by a 3 kW immersion heater in 45 minutes?
Energy = Power x time = 3000 x 45 x 60
= 8 100 000 = 8.1 MJ
You will find that all appliances
in the home that give out heat operate at quite high powers and therefore consume a lot of
energy.
USE OF ELECTRICAL
ENERGY |
|
WHAT CAN YOU DO FOR 15p |
|
| Electric cooker |
4 units per day |
Watch TV for 3 hours |
Drill for 4 hours |
|
10 m3 freezer |
15 units per week |
Toast 70 slices of bread |
Mix 60 cakes |
| Electric iron |
0.5 units per hour |
Warm a bed for a week |
|
|
Washing machine |
9 units per week |
Use a vacuum cleaner for 2 hours |
|
| Unlagged hot water tank |
160 units per week |
Run an electric clock for 3 months |
|
|
Lagged hot water tank |
80 units per week |
|
|
PROBLEMS
1. Copy and complete the following
table:
In this table take the cost of one unit to be 8p
| Power and appliance |
Time |
Energy (J) |
Cost (p) |
| 2 kW fan heater |
2 hours |
|
|
| 200 W light bulb |
|
|
15 |
| 60W light bulb |
5 hours |
|
|
| 3 kW immersion heater |
|
|
30 |
| 2 kW kettle |
5 minutes |
|
|
| 150 W stereo |
40 minutes |
|
|
| 25 W motor |
20 minutes |
|
|
| 500 W cleaner |
|
|
7.5 |
| 300 W hair drier |
5 minutes |
|
|
| 250 W drill |
40 minutes |
|
|
| 30 W radio |
|
|
2 |
| 120 W TV |
|
|
2 |
| 400 W iron |
|
|
22.5 |
| 7 kW shower |
3 minutes |
|
|
| 300 W mower |
30 minutes |
|
|
| 75 W electric blanket |
|
|
45 |
| 2 kW cooker ring |
20 minutes |
|
|
| 2.5 kW oven |
3 hours |
|
|
| 750 W radiator |
10 hours |
|
|
| 20 W CD player |
40 minutes |
|
|
2. Why will the energy used by the
fridge in a normal house in a year be much less that the amount that you have worked
out?
A VERSION IN WORD IS AVAILABLE ON THE SCHOOLPHYSICS USB