

The
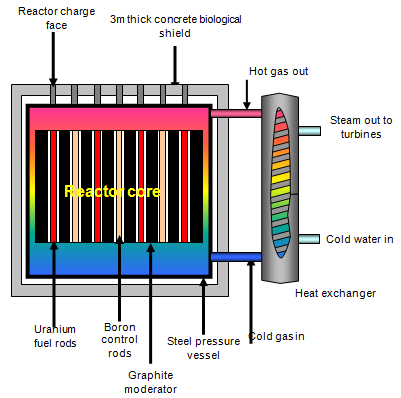
CORE of the reactor contains the uranium fuel (an alpha
emitter and not very dangerous if handled with care) that is held in thousands of metal tubes
in a large block of graphite. The graphite, called the
MODERATOR slows down the neutrons emitted at each
fission so that they can react better. Carbon dioxide gas is blown through the reactor core
under pressure to take away the heat energy produced by the fission reactor. This gas is
then passed over tubes containing water, giving out its heat and turning the water into high
temperature steam which is then used to drive turbines and generators. To increase or
decrease the output power of the reactor a large number of CONTROL
RODS are used. These are made of boron or boron-steel that gobble up
neutrons. They can be lowered into the reactor to reduce the number of neutrons and so
lower the power or they can be raised to increase the power.
When the nucleus
splits we get two smaller nuclei, two or three neutrons and some energy. This energy
appears as heat due to the kinetic energy of the smaller nuclei and the neutrons.
The
energy is produced because the mass of the uranium nucleus plus the mass of the incoming
neutron is slightly greater than the masses of the particles formed after fission.
You
don't get very much energy from splitting one uranium nucleus but in one kilogram of
uranium there are around a million million million million million nuclei and if you could split all
of them the energy produced would be very large. In fact if all the nuclei in 1 kg of uranium
235 could be split the energy produced would be about the same as that obtained from
burning three thousand tons of coal!
The whole reactor core is contained in a steel
pressure vessel and then surrounded by a thick layer of concrete to protect the workers from
radiation.
Location, benefits and drawbacks of nuclear power stations
Location
The reactor is a very heavy structure
and so it is important that nuclear power stations are built on very stable solid rock.
They
need large amounts of water to turn to steam to drive the turbines and also as coolant in the
condensing units and so they should be built near the sea, a river estuary or a large
lake.
People are not usually too happy about living near a nuclear reactor and so nuclear
power stations are usually built in areas of low population.