Thermal conductivity and
kinetic theory
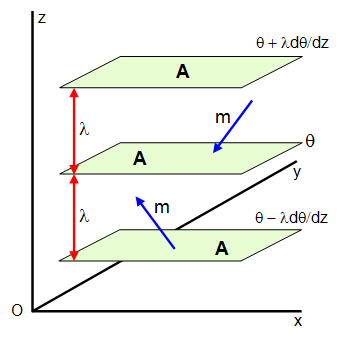
Consider three horizontal planes in the gas each of area A. The heat
conducted downwards through A per second is then -kAdθ/dx
However, each second a mass of
gas m at a temperature θ
1 crosses A moving downwards and a mass of gas
m at a temperature θ
2 crosses A moving upwards.
Now:
m = ρcA/6
θ
1
= θ + λdθ/dz and θ
2 = θ + λdθ/dz
Therefore, since heat = mcθ , the net transfer of heat
downwards is:
–[ρcA/6]λ[2dθ/dz]C
v.
But this must equal –kAdθ/dz and therefore:
k =
1/3ρcλC
v and since η = 1/3[ρcλ] k = ηC
v
Thermal conductivity of a gas: k = ηCv
WORD VERSION AVAILABLE ON THE SCHOOLPHYSICS CD

 Consider three horizontal planes in the gas each of area A. The heat
conducted downwards through A per second is then -kAdθ/dx
Consider three horizontal planes in the gas each of area A. The heat
conducted downwards through A per second is then -kAdθ/dx