
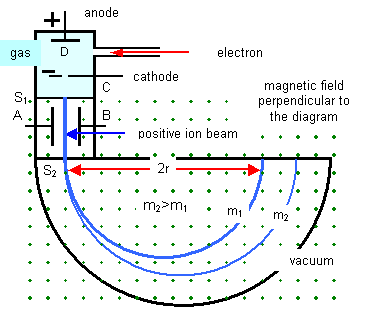
Ions are formed at D and pass through the cathode C and then through a slit S1. They then travel between two plates A and B, between which a potential (V) is applied.
A magnetic field (strength B) is applied at right angles to the electrostatic field and so the electrostatic and electromagnetic forces act in opposite directions to each other.
A particle with a charge q and velocity v will only pass through the next slit S2 if the resultant force on it is zero – that is it is travelling in a straight line. That is if:
| Electromagnetic force (Bqv) = Electrostatic force (qE) Velocity of particle (v) = E/B |
| Mass of ion (M) = rB2q/E |