
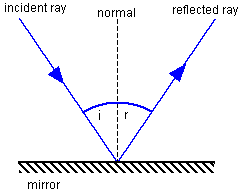
The reflection of light from a plane mirror can be summarised by the following laws:
1. The angle of incidence (i) is equal to the angle of reflection (r)
2. The incident ray, reflected ray and the normal to the surface at the point of incidence all lie in the same plane.
The reflection from a plane (flat) mirror is shown with the normal line at right angles to the mirror and the use of shading to represent the back of the mirror.
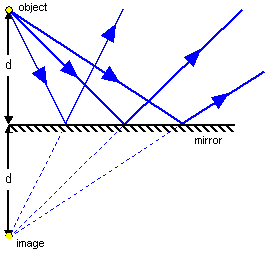
Images
There are two types of image:
(a) Real Image
This is one through which the light rays actually pass and which can be formed on a screen. Examples of real images are the image formed on the film in a camera or on the retina of your eye
(b) Virtual Image
This is one through which the rays do not pass, they only appear to come from it.
Examples of virtual images are the image formed by a magnifying glass when used to look at a small object and that in a plane mirror.
For a real object, the image produced by a plane mirror is virtual and the same distance (d) behind the mirror as the object is in front of it.