
When a force (F) is applied to an
object of mass m for a certain length of time (t) the object experiences an impulse
(Ft) and the result of this is that the momentum of the object changes by an amount
mDv where Dv is the
change of velocity of the object.
If the object changes its velocity from u to v
as a result of the impulse then:
If is very easy to show this impulse and
the resulting change of momentum using an Ft graph.
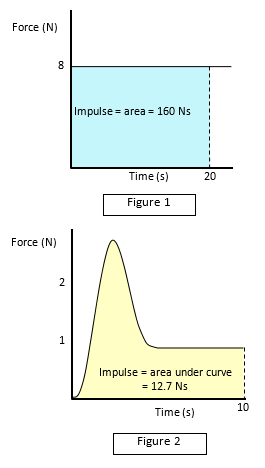
The graph in Figure 1 shows a constant force (F
= 8 N) being applied to an object. The impulse experienced by the object in a time t
(=20s) is Ft (160 Ns), but this is the area under the line.
The same argument
holds when the force on the object is not constant. Figure 2 shows an Ft graph of the
thrust on a small firework rocket plotted against time. The momentum change of the
rocket is the area under the Ft curve.