
Newton described the elasticity of the collision by considering the velocities of approach and recession as shown in the following diagram.
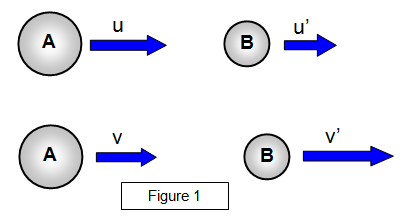
This is known as Newton's
Law of impact.
The ratio [v' – v]/[u' – u] must always be less than one except for
a perfectly elastic collision where it is equal to 1. For a perfectly inelatic collision e =
0.
This means that in a perfectly elastic collision the velocity of approach of the
two bodies before the impact is equal to their velocity of separation after the
impact.